Relocating to Europe can be an exciting and overwhelming experience. Among the most frequently used queries posed by expats is the following one: What is the difference between immigration vs emigration? Knowledge of these terms is critical to all individuals intending to move to a foreign country because it influences it in terms of legal documentation to residency regulations.
This guide is aimed at shedding light on Immigration vs Emigration, clarifying the issues that you may encounter, and giving you a step-by-step road map of the expats who are going to Europe. At the end of this guide, you shall be in a clear position on how to go about ensuring that your move is smooth, legal, and stress-free.
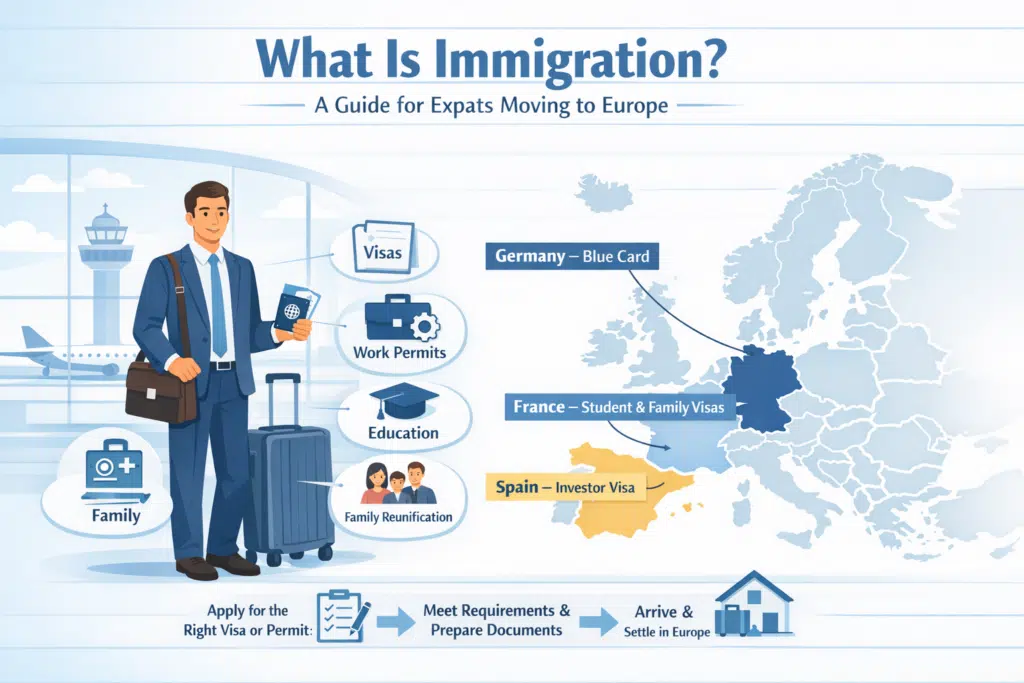
What is Immigration?
Immigration is the act of going into an unfamiliar nation in a bid to spend some time in it, either temporarily or permanently. It is considered in relation to the destination country.
Key Features of Immigration
- Concentrated on the entry into a new country.
- Needs legal papers such as work permits, residency permits, or visas.
- Maybe because of work, schooling, family reunion, business, or investment.
Immigration is different in Europe. For instance:
- Germany provides visas of Blue Card visa to highly qualified employees.
- France has certain student and family reunification visa.
- Spain will offer investor visas to individuals initiating business or buying property.
Immigration laws can be explained so that learning them before moving results in you being able to stay during the entire period in a completely legal manner, and prevents the possibility of fines and deportation.
What is Emigration?
On the other hand, emigration is defined as the practice of abandoning your country of origin so as to move to a different country. It is perceived in view of your home country.
Key Features of Emigration
- Preoccupied with abandoning the motherland.
- Needs the writing of documentation, exit permits (where necessary), and financial planning.
- Driven by improved opportunities, safety, improvement of lifestyle, or education.
The initial phase of the larger process of international mobility is usually emigration. Unless they do their planning, expatriates can encounter legal or financial obstacles even before they get to Europe.
Immigration vs Emigration – Key Differences
| Feature | Immigration | Emigration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Entering a foreign country to live | Leaving your home country to live abroad |
| Perspective | Host country’s view | Home country’s view |
| Legal Requirement | Visa, work permit, residency | Exit permits, legal documents |
| Purpose | Work, study, family, business | Better opportunities, lifestyle, safety |
| Example | Moving to Germany for a job | Leaving a country to move to Germany |
This difference is very important to expats to immigration vs emigration since everything, such as visa applications, tax, access to medical services, and other local provisions, is influenced by this difference.
Read Also: Italian Embassy Visa Application 2026: Avoid Rejection Fast
Temporary vs Permanent Visas (Immigrant vs Non-Immigrant)
It is important to know the distinction between temporary (non-immigrant) and permanent (immigrant) visas before expats relocate to Europe. The kind of visa you select influences your duration of stay, right of work, family, alternative, and permanent settlement.
Temporary (Non-Immigrant) Visas
A temporary visa is a temporary stay in one of the European countries for a certain purpose and for a limited time.
Common reasons include:
- Work on a fixed-term contract
- Short-term or study education.
- Business/professional visits.
- Tourism or family visits
Key points:
- Valid months or several years.
- Limited work or study rights
- County extensions are based on country rules.
- Does not directly result in permanent residence.
A number of expats obtain temporary visas with the intention of becoming permanently settled.
Permanent (Immigrant) Visas
A permanent visa enables you to stay in Europe permanently or long-term, and it is the best option in you intend to settle there.
Common pathways include:
- Long-term employment
- Family reunification
- Investment programs or business programs.
Key points:
- Long-term residency rights
- Unlimited access to work, medical services, and education.
- Leads to permanent residence or citizenship over time
Permanent visas offer stability, security, and opportunities.
Immigration vs Emigration Matters for Expats
Moving to Europe is not a simple process of boarding an aircraft. Confusion of the two terms will result in:
- Wrong visa applications.
- Sluggishness in acquiring residency.
- Legal penalties or fines
- Access to healthcare, banking, or social services is a challenge.
Once the difference is understood clearly, you can strategize and make your move effectively, eliminate unwarranted stress, and quickly settle in your new country.
Step-by-Step Guide for Expats Moving to Europe
Coming to a foreign country can be a challenging task, but it can be divided into distinct steps that are easy to manage. These are the steps that expatriates can take:
1. Research Your Destination Country
Read about the country you are going to before you move to it:
- Know the immigration regulations, visa programs, and immigration status.
- Evaluate the employment opportunities, the price of houses, medicine, and the quality of life.
- Identify language requirements and cultural norms
An example something to look at is that Germany may demand evidence of financial stability to grant the visa, whereas Spain can demand evidence of property or rent. Prior research is always time-saving, and it avoids surprises.
2. Check Visa Requirements
Depending on the purpose of your move, your type of visa is:
- Work Visa: Professionals having job offers.
- Student Visa: For academic studies or research
- Family Visa: Family reunification.
- Investor Visa: For business starters or those who are buying property.
Gather necessary documents, such as:
- Passport
- Professional and academic certificates.
- Proof of income or financial stability
- Letters of acceptance (students).
Applying early increases your chances of approval and avoids delays.
3. Prepare Documentation
The emigration and immigration are required to be properly documented:
- Identity documents (passport, birth certificate)
- University diplomas and translations.
- Employment records
- Medical records and immunization.
Make sure that all the documents are verified, translated, and notarized where necessary. This minimizes the chances of a visa being rejected or taking a long time at the border.
4. Apply for a Visa / Residency
Send your application via the Internet or to the corresponding embassy:
- Properly filled application forms.
- Pay required fees
- Quickly respond to any questions or other paperwork requests.
It is important to keep track of your application and be organized. Online visa tracking systems are available in some European countries, and this takes away the inconvenience.
5. Plan Your Move
Once your visa is approved, plan your logistics:
- Temporarily book a place to stay and book flights.
- Pack in advance, based on the baggage limitations of the airline and the customs regulations.
- Make your arrangements in banking, mobile, and healthcare in your destination country.
Preplanning will help to relieve stress and make the initial few weeks in Europe go smoothly.
6. Settle and Adapt
Assimilation in a new country is not limited to legal adherence:
- Learn the local language, even basic phrases, to help
- Understand local laws, customs, and cultural norms
- Form expat groups or communities.
- Research job opportunities, networking programs, and social integration programs.
Through integration at an early age, you are able to establish a successful personal and professional life in your new country.

Common Challenges Expats Face & How to Overcome Them
Despite preparation, expats can still be faced with challenges. Here’s how to overcome them:
Language Barrier
- Study languages or study using mobile applications.
- Check with the locals or other expats to enhance communication.
Legal Documentation
- Double-check visa and residency requirements
- Duplicate every piece of paperwork.
- In complicated cases, it may be wise to seek the services of a migration attorney.
Cultural Adjustment
- Cultural norms and etiquette of research.
- Participate in local events/ workshops.
- Relate with expat communities to get tips and help.
Housing & Banking
- Purchase temporary accommodation in advance.
- Open a local bank account at once, for convenience.
- Research medical and health insurance.
With the anticipation of such challenges, the expats will be able to adjust more quickly and make the move a stress-free experience.
Read Also: Do US Citizens Need a Visa for Greece?
Final Words
To move to Europe successfully, it is necessary to understand the distinction between immigration vs emigration. With this step-by-step guide, you are able to save yourself from legal troubles and make a comfortable settlement, and begin your expat journey without any doubt.
Europe has unlimited opportunities for career development, education, and personal development. You should not wait any longer; you should begin your research, you should make your documents ready, and you should take the first step to your European adventure!